Summary of Jonathan Haidt’s Moral Foundations Theory and Differences Between the Left and Right
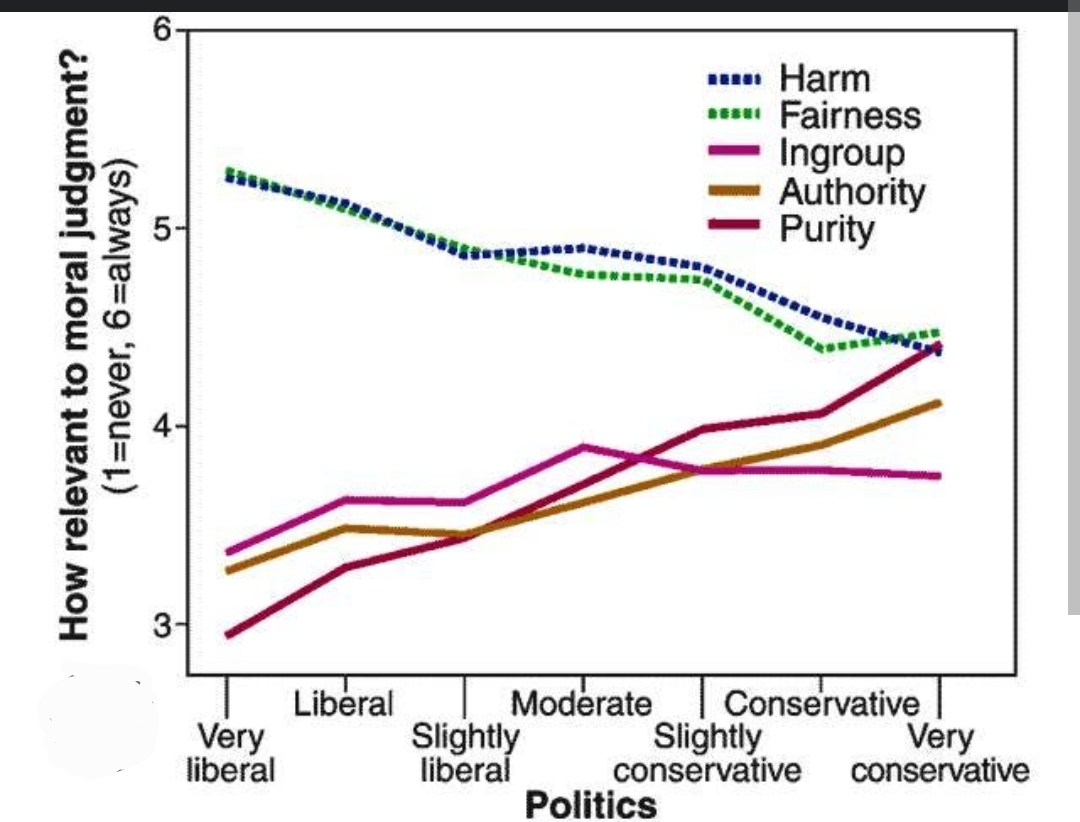
Jonathan Haidt’s Moral Foundations Theory provides a framework for understanding how the left and right prioritize different moral values. He identifies five core moral foundations and shows how liberals and conservatives weigh them differently.
The Five Moral Foundations
Care:
- Definition: Compassion and prevention of suffering.
- Rooted in: Evolutionary nurturing instincts and attachment systems.
- Political Divide:
- Left: High priority on care, emphasizing empathy and protecting the vulnerable.
- Right: Values care, but balanced with other moral principles.
Fairness:
- Definition: The idea of justice, cooperation, and preventing cheating.
- Rooted in: Evolutionary benefits of reciprocal altruism and proportionality.
- Political Divide:
- Left: Defines fairness as equality of outcomes (everyone gets the same share).
- Right: Defines fairness as proportionality (people get what they earn).
Loyalty:
- Definition: Commitment to one’s in-group, tribe, or nation.
- Rooted in: Evolutionary need for coalition-building and social unity.
- Political Divide:
- Left: Devalues loyalty, seeing it as exclusionary and often as a form of racism.
- Right: Strongly values loyalty, emphasizing patriotism and national unity.
Authority:
- Definition: Respect for hierarchy, tradition, and social order.
- Rooted in: Primate social structures and historical leadership roles.
- Political Divide:
- Left: Skeptical of authority, seeing it as oppressive or unjust.
- Right: Respects authority, believing it brings order and stability.
Purity:
- Definition: Focuses on avoiding physical and moral contamination.
- Rooted in: Evolutionary disgust response and self-discipline.
- Political Divide:
- Left: Downplays purity, focusing instead on inclusivity and tolerance.
- Right: Values purity, emphasizing self-control, discipline, and spiritual cleanliness.
Key Political and Moral Differences
Different Views on Fairness
- Liberals: Fairness = equality of outcome (everyone gets the same resources).
- Conservatives: Fairness = proportionality (people get what they work for).
- Liberal Policies Reflecting This View:
- Support for progressive taxation and welfare programs to reduce inequality.
- Conservative Policies Reflecting This View:
- Opposition to wealth redistribution (believe it unfairly penalizes hard work).
Different Views on Loyalty and Authority
- Liberals:
- View loyalty as morally irrelevant or even dangerous (can lead to exclusion or racism).
- Oppose patriotism and nationalism, favoring inclusivity.
- Skeptical of authority structures (e.g., government, police, military).
- Conservatives:
- Strongly value loyalty (e.g., patriotism, national pride, group cohesion).
- View authority as necessary for social stability.
- Real-World Effects:
- Liberals favor anti-establishment movements, activism, and pushing for structural change.
- Conservatives support tradition, law enforcement, and hierarchical institutions.
Different Views on Compassion
- Liberals:
- More universalist—concerned with global humanitarian issues (e.g., refugees, animal rights).
- Compassion extends beyond immediate community.
- Conservatives:
- More localist—focus on helping their own community (e.g., veterans, local charities).
- Compassion is balanced with loyalty and responsibility.
Psychological and Personality Differences
Openness to Experience
- Liberals:
- Score higher on openness.
- Enjoy novelty, change, diversity, and cultural variety.
- Favor open borders and multiculturalism.
- Conservatives:
- Score lower on openness.
- Prefer tradition, stability, and familiarity.
- Favor closed borders to preserve culture and social order.
- Evolutionary Reasoning:
- Historically, new tribes often brought danger (war, disease, or conflict), so conservatives are more cautious about outsiders.
- Liberals focus on potential benefits of new experiences.
Conscientiousness (Orderliness and Discipline)
- Liberals:
- Score lower in conscientiousness.
- Believe inequality is caused by unjust systems rather than personal effort.
- Support policies that redistribute wealth to correct unfair systems.
- Conservatives:
- Score higher in conscientiousness.
- Believe hard work and discipline lead to success.
- Oppose policies that redistribute resources from hardworking people to those who haven’t earned them.
Agreeableness (Compassion vs. Politeness)
- Liberals:
- Score higher in compassion—care more for underdogs and marginalized groups.
- Conservatives:
- Score higher in politeness—care more about respecting traditions and authority.
Summary of Key Differences
| Moral Foundation | Liberals (Left) | Conservatives (Right) |
|---|---|---|
| Care | High priority, universalist compassion | Balanced with other values, care for in-group |
| Fairness | Equality of outcome (redistribution) | Proportionality (reward for effort) |
| Loyalty | Low priority, seen as exclusionary | High priority, patriotism and group unity |
| Authority | Low priority, skepticism of hierarchy | High priority, respect for tradition |
| Purity | Low priority, inclusivity over discipline | High priority, self-discipline and moral purity |
| Psychological Trait | Liberals (Left) | Conservatives (Right) |
|---|---|---|
| Openness to Experience | High, love novelty and diversity | Low, prefer tradition and stability |
| Conscientiousness | Low, see inequality as systemic | High, believe in effort-based success |
| Agreeableness (Compassion vs. Politeness) | High in compassion | High in politeness |
Conclusion: The Core Divide Between Left and Right
- Liberals prioritize care, equality, and openness, leading to progressive policies and global humanitarian efforts.
- Conservatives value tradition, loyalty, proportional fairness, and order, leading to patriotism, respect for authority, and structured communities.
- Personality differences explain why each group sees the world so differently and often misunderstands the other’s moral priorities.
Jonathan Haidt’s Moral Foundations Theory helps explain why liberals and conservatives think the way they do, showing that neither side is inherently wrong—they just prioritize different values.
Moral Foundations Theory Questionnaire
This questionnaire is designed to assess how you prioritize different moral values based on Jonathan Haidt’s Moral Foundations Theory. Please rate each statement on a scale of 1 to 5, where:
1 = Strongly Disagree
2 = Disagree
3 = Neutral
4 = Agree
5 = Strongly Agree
1. Care (Compassion & Prevention of Harm)
- ☐ It is important to prevent suffering, even if it requires sacrificing personal interests.
- ☐ I feel strong emotional distress when I see someone in pain.
- ☐ Society should prioritize the needs of the weak and vulnerable.
- ☐ I believe policies should be designed primarily to reduce suffering.
- ☐ Even when rules are broken, I think showing kindness is more important than punishment.
2. Fairness (Justice & Equality vs. Merit & Proportionality)
- ☐ People should receive equal opportunities, regardless of background or effort.
- ☐ It is unfair when people work hard but do not get ahead in life.
- ☐ Success should be based on effort rather than luck or privilege.
- ☐ Everyone should be treated equally, even if that means redistributing wealth.
- ☐ If two people put in different levels of effort, they should receive different rewards.
3. Loyalty (In-Group Commitment & Patriotism)
- ☐ Loyalty to my country, family, or group is more important than individual interests.
- ☐ It is important to stand by your group, even if they have made mistakes.
- ☐ Betraying one’s group or country is one of the worst moral offenses.
- ☐ I feel strong emotions when I see my country’s flag or hear my national anthem.
- ☐ People who criticize their own country in front of outsiders are disloyal.
4. Authority (Respect for Leadership & Social Order)
- ☐ Societies function best when people respect traditions and established authorities.
- ☐ Parents and teachers should be obeyed without question.
- ☐ Laws and rules should be followed, even if they seem unfair.
- ☐ A society without strong leadership will fall into chaos.
- ☐ Disrespecting authority figures is a sign of moral decline.
5. Purity (Sanctity, Self-Control, & Moral Integrity)
- ☐ Some actions are morally wrong, even if they don’t directly harm anyone.
- ☐ Purity and self-discipline are important aspects of a good life.
- ☐ Certain traditions and rituals are sacred and should not be changed.
- ☐ People should strive to avoid crude or impure behavior.
- ☐ Moral decay is one of the biggest threats to society.
Scoring and Interpretation
Step 1: Calculate Scores for Each Moral Foundation
- Add up your responses for each category (Care, Fairness, Loyalty, Authority, Purity).
- Each category has a maximum possible score of 25 and a minimum of 5.
Step 2: Interpret Your Results
- Higher Scores (20-25): You strongly value this moral foundation.
- Moderate Scores (12-19): You somewhat value this foundation but do not prioritize it above others.
- Lower Scores (5-11): This moral foundation is less important to you.
Step 3: Compare with Political Leanings
- Liberals tend to score highest on Care & Fairness and lower on Loyalty, Authority, and Purity.
- Conservatives tend to score more evenly across all five foundations, especially valuing Loyalty, Authority, and Purity.
- Libertarians tend to prioritize Fairness (as proportionality) and Authority (as personal freedom) while scoring lower on Care and Loyalty.
Reflection Questions
- Which moral foundation did you score the highest on? What does this say about your values?
- Did your results align with your political or social views?
- How do you think these moral foundations influence debates in politics, culture, and society?
- If you scored low in some areas, do you think society overvalues or undervalues those moral foundations?
This questionnaire can help you understand how your moral intuitions shape your worldview and how others might see morality differently!






One Response
So no results for an anarchist? From this article it would seem the moderate are the “best” but I think in reality the moderates have simply drank the CoolAid and the BudLight. And I think the author would agree that the “best” is subjective to the wants of the individual… ultimately we are choosing 1984 or Brave New World. Choosing Anarchy is choosing neither ending; but the uncertainty of free choices.